Time Series Analysis on Air Passenger Data

Time series analysis is crucial for understanding trends, seasonality, and making future predictions based on historical data. In this blog, we will analyze the famous AirPassengers dataset, perform decomposition, check for stationarity, build an ARIMA model for forecasting, and detect anomalies.
Goal
Our goal is to analyze the AirPassengers dataset to:
- Identify trends and seasonal patterns.
- Check stationarity of the dataset.
- Build an ARIMA model for forecasting.
- Detect anomalies in the data.
Required Packages
Before we start, install the necessary Python packages:
pip install pandas matplotlib statsmodels numpyStep 1: Load and Inspect the Data
We first load the dataset and inspect its structure.
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from statsmodels.tsa.seasonal import seasonal_decompose
import numpy as np
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller
from statsmodels.tsa.arima.model import ARIMA
# Load dataset
df = pd.read_csv("AirPassengers.csv", parse_dates=["Month"], index_col="Month")
# Display first few rows
print(df.head())
print(df.info()) Step 2: Data Visualization
Plot the data to understand trends and seasonality.
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
plt.plot(df.index, df["#Passengers"], label="Monthly Passengers")
plt.xlabel("Year")
plt.ylabel("Passengers (in thousands)")
plt.title("Air Passenger Traffic Over Time")
plt.legend()
plt.show() 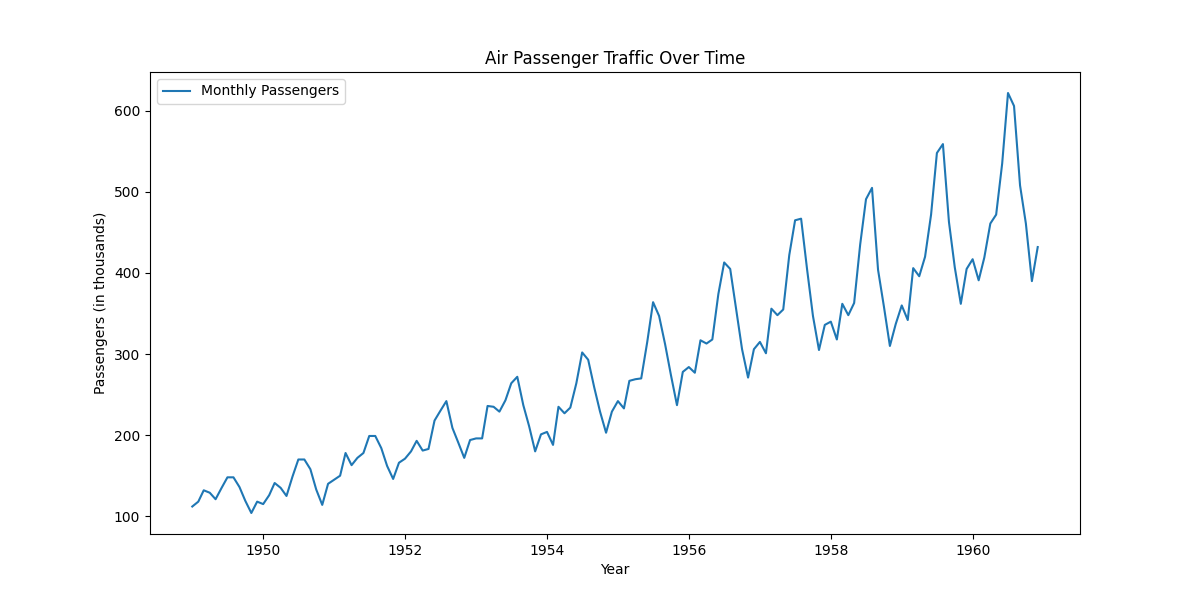
Step 3: Handle Missing Values
print(df.isnull().sum()) # Check for missing values
df = df.fillna(method="ffill") # Forward fill if necessaryStep 4: Decomposing the Time Series
We decompose the time series into trend, seasonal, and residual components.
# Decomposing the time series
decomposed = seasonal_decompose(df["#Passengers"], model="multiplicative", period=12)
# Plot the decomposition
decomposed.plot()
plt.show() 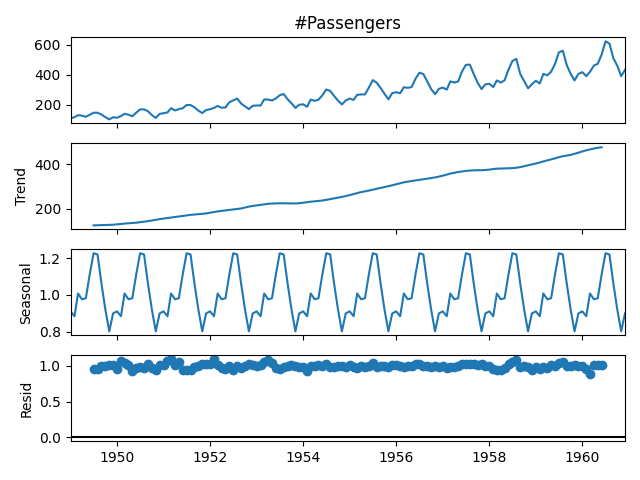
Step 5: Test for Stationarity (ADF Test)
We use the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test to check stationarity.
result = adfuller(df["#Passengers"])
print(f"ADF Statistic: {result[0]}")
print(f"P-value: {result[1]}") If the p-value is greater than 0.05, the data is non-stationary.
To make the series stationary, we apply differencing:
df["Passengers_diff"] = df["#Passengers"].diff().dropna()
# Re-run ADF test
result = adfuller(df["Passengers_diff"].dropna())
print(f"New ADF Statistic: {result[0]}")
print(f"New P-value: {result[1]}") Step 6: Train-Test Split
train_size = int(len(df) * 0.8)
train, test = df.iloc[:train_size], df.iloc[train_size:] Step 7: Train an ARIMA Model
# Train ARIMA Model
model = ARIMA(train["#Passengers"], order=(1,1,1))
model_fit = model.fit()
# Forecast
forecast = model_fit.forecast(steps=len(test))
# Plot results
plt.plot(test.index, test["#Passengers"], label="Actual")
plt.plot(test.index, forecast, label="Forecast", linestyle="dashed")
plt.legend()
plt.show() 
Step 8: Detecting Anomalies using Z-Score
df["Z-Score"] = (df["#Passengers"] - df["#Passengers"].mean()) / df["#Passengers"].std()
df["Anomaly"] = df["Z-Score"].abs() > 3 # Mark anomalies if Z-score > 3
# Plot anomalies
plt.plot(df.index, df["#Passengers"], label="#Passengers")
plt.scatter(df.index[df["Anomaly"]], df["#Passengers"][df["Anomaly"]], color="red", label="Anomalies")
plt.legend()
plt.show() 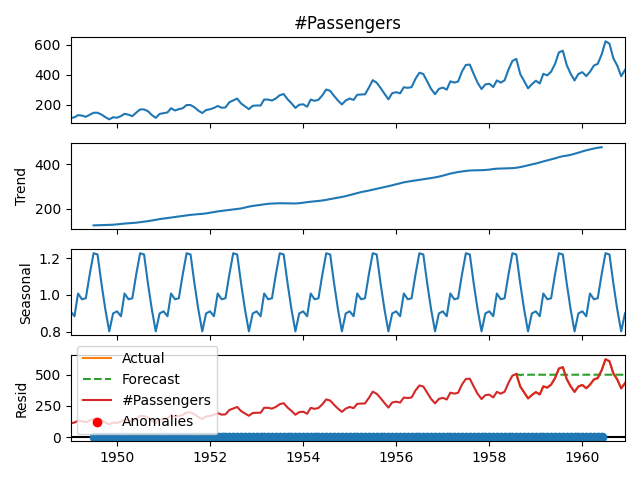
Conclusion
In this analysis, we:
- Visualized the data to identify trends and seasonality.
- Checked for stationarity and made adjustments.
- Built an ARIMA model for forecasting future values.
- Detected anomalies using Z-Score. This approach can be applied to any time series dataset to gain insights and make informed decisions.
Full Code
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from statsmodels.tsa.seasonal import seasonal_decompose
import numpy as np
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller
from statsmodels.tsa.arima.model import ARIMA
# Load dataset
df = pd.read_csv("AirPassengers.csv", parse_dates=["Month"], index_col="Month")
# Handle missing values
df = df.fillna(method="ffill")
# Visualization
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
plt.plot(df.index, df["#Passengers"], label="Monthly Passengers")
plt.xlabel("Year")
plt.ylabel("Passengers (in thousands)")
plt.title("Air Passenger Traffic Over Time")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Decomposing the time series
decomposed = seasonal_decompose(df["#Passengers"], model="multiplicative", period=12)
decomposed.plot()
plt.show()
# ADF Test
result = adfuller(df["#Passengers"])
print(f"ADF Statistic: {result[0]}")
print(f"P-value: {result[1]}")
# Differencing
df["Passengers_diff"] = df["#Passengers"].diff().dropna()
result = adfuller(df["Passengers_diff"].dropna())
print(f"New ADF Statistic: {result[0]}")
print(f"New P-value: {result[1]}")
# Train-Test Split
train_size = int(len(df) * 0.8)
train, test = df.iloc[:train_size], df.iloc[train_size:]
# Train ARIMA Model
model = ARIMA(train["#Passengers"], order=(1,1,1))
model_fit = model.fit()
forecast = model_fit.forecast(steps=len(test))
plt.plot(test.index, test["#Passengers"], label="Actual")
plt.plot(test.index, forecast, label="Forecast", linestyle="dashed")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Detect Anomalies
df["Z-Score"] = (df["#Passengers"] - df["#Passengers"].mean()) / df["#Passengers"].std()
df["Anomaly"] = df["Z-Score"].abs() > 3
plt.plot(df.index, df["#Passengers"], label="#Passengers")
plt.scatter(df.index[df["Anomaly"]], df["#Passengers"][df["Anomaly"]], color="red", label="Anomalies")
plt.legend()
plt.show() Random Blogs
- How to Become a Good Data Scientist ?
- Data Analytics: The Power of Data-Driven Decision Making
- Convert RBG Image to Gray Scale Image Using CV2
- Mastering SQL in 2025: A Complete Roadmap for Beginners
- What is YII? and How to Install it?
- The Ultimate Guide to Data Science: Everything You Need to Know
- Extract RGB Color From a Image Using CV2
- Government Datasets from 50 Countries for Machine Learning Training
- AI & Space Exploration – AI’s Role in Deep Space Missions and Planetary Research
- 5 Ways Use Jupyter Notebook Online Free of Cost
Prepare for Interview
- JavaScript Interview Questions for 5+ Years Experience
- JavaScript Interview Questions for 2–5 Years Experience
- JavaScript Interview Questions for 1–2 Years Experience
- JavaScript Interview Questions for 0–1 Year Experience
- JavaScript Interview Questions For Fresher
- SQL Interview Questions for 5+ Years Experience
- SQL Interview Questions for 2–5 Years Experience
- SQL Interview Questions for 1–2 Years Experience
- SQL Interview Questions for 0–1 Year Experience
- SQL Interview Questions for Freshers
- Design Patterns in Python
Datasets for Machine Learning
- Awesome-ChatGPT-Prompts
- Amazon Product Reviews Dataset
- Ozone Level Detection Dataset
- Bank Transaction Fraud Detection
- YouTube Trending Video Dataset (updated daily)
- Covid-19 Case Surveillance Public Use Dataset
- US Election 2020
- Forest Fires Dataset
- Mobile Robots Dataset
- Safety Helmet Detection
- All Space Missions from 1957
- OSIC Pulmonary Fibrosis Progression Dataset
- Wine Quality Dataset
- Google Audio Dataset
- Iris flower dataset
- Artificial Characters Dataset
- Bitcoin Heist Ransomware Address Dataset





